Security is an ever-present topic in our modern lives, from intimate relationships to global trade agreements and from physical security measures to cyber threats. Security plays an essential role in maintaining both our well-being and assets while upholding confidence; in this article, we’ll delve into its many facets – its evolving significance & its critical place within today’s complex interlinked society.
Section I : Understand Security Fundamentals
Security in its broadest sense means being safe against various risks or damage; this includes but is not limited to financial, national, personal cyber and environmental security. Security therefore protects stability, safety and the things valued most in life.
1.2 The Historical Development of Security Over time, security has changed considerably. In ancient times it primarily involved physical protection against immediate dangers like wild animals or hostile tribes; with societies developing and expanding they would add fortifications, armies and legal systems as measures against both internal and external threats.
Due to technological developments and globalization, security has developed at unprecedented speeds over recent decades. National security encompasses protection from military aggression and cyberattacks as well as environmental concerns like climate change; while personal security extends far beyond physical safety to protect data privacy and guard against cyber-attacks.
Security can be broken down into various subcategories depending on which domain they address:
1.3.1 Physical Security
Physical security encompasses measures taken to protect people, property, and assets against threats such as vandalism, theft or natural catastrophes. Examples of security systems that help ensure protection include surveillance cameras, access controls systems and secure building designs.
1.3.2 National Security
National security refers to safeguarding a nation and its people against all forms of threats both internal and external to it, from any military attack by foreign armies as well as strategies developed specifically against terrorist threats. This encompasses everything from protection against military assault and intelligence gathering activities through to countering strategies against acts of terrorism.
1.3.3 Cybersecurity
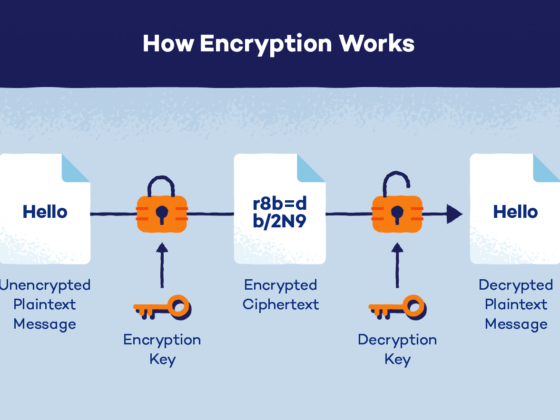
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of safeguarding electronic systems and information from hacking attempts and unauthorised access. Various cybersecurity measures – such as firewalls and encryption software as well as antivirus solutions and best practices that enhance online conduct – exist to achieve this end.
Also Read: understanding-software-as-a-service-saas-revolutionizing-the-software-industry
1.3.4 Financial Security
Financial security refers to the management and protection of one’s financial resources and assets. It encompasses measures like budgeting savings investing and insuring to secure long-term stability as well as future planning.
1.3.5 Environmental Security
Environmental security involves safeguarding Earth’s ecosystems and natural resources against threats like pollution, climate change and resource depletion to ensure sustainable future for humanity as a whole.
1.3.6 Personal Security
Personal security refers to protecting both physical and health safety against threats such as harassment, crime and domestic violence.
Section 2: What Security Means in the Digital Era
Digital technology has dramatically transformed security. Thanks to web browsing, smart device use, and digitization of critical systems our lives are increasingly intertwined with that world; creating both challenges and complications when it comes to security.
Cybersecurity Has Been Recognized As Essential In today’s digital era, cybersecurity has emerged as an integral element of security. Cybersecurity refers to protecting computers and networks against various forms of threats including ransomware, malware, hackers and data breach attacks; its significance cannot be overemphasized given how our technological dependence leaves us more susceptible than ever before to cyberattacks.
2.2.1 Key Elements of Cybersecurity.
Authentication and Access Control are integral parts of cyber security; both serve to ensure that only authorized people or systems can gain entry to sensitive data.
Data Encryption Secure your sensitive information via encryption so that only authorized people are able to decrypt it.
Interceptors, Firewalls and Security Systems offer protection from unauthorised access and can detect suspicious activities across networks.
Regular updates: Patching software vulnerabilities to defend against attacks by hackers.

Educational for Users: Raising awareness and offering best practices that reduce security risks related to human beings such as phishing attacks.
Also Read: swot-analysis-how-to-with-table-and-example
Privacy and Data Security Securing sensitive and personal data in today’s technological environment is also of utmost importance, with individuals as well as businesses alike having so much personal data stored online requiring protection to avoid financial loss, identity theft or harm to reputations from data breaches that occur online.
2.3.1 Data Security Measures
To safeguard sensitive information against unintended access by third-parties, encryption of files is an integral component. Even should they fall into untrustworthy hands, data remains inaccessible if breached or stolen.
Secure Authentication Secure and unique passwords, multi-factor authentication and biometric verification provide layers of protection to data access.
Data backup provides assurance in case data loss or ransomware attacks occur and can ensure its restoration.
Compliance With Regulations It is vitally important for individuals and companies alike to observe regulations and laws related to data protection such as GDPR for Europe or HIPAA for America in order to remain ethical and legal compliant.
Section 3 : Importance of Security
Security is of vital importance both on the individual and global levels. States invest billions of dollars each year into diplomacy and defense to reduce conflicts and foster coexistence; individuals take steps to secure their families and homes and promote feelings of safety and peace within their homes and neighborhoods.
Security plays an essential part in creating economic prosperity. A secure environment attracts investments, stimulates economic expansion and provides jobs. Furthermore, cybersecurity protects banks and businesses against cyber threats which threaten operations or cause losses of their financial data.
Protecting Human Rights
Security is inextricably tied to humans’ rights and protecting these is critical. Ensuring security means preserving freedom, life and privacy for everyone; combatting discrimination based on gender; eliminating violence against women and creating an equitable and just society are also central goals in providing security.
Environmental Sustainability Protecting our planet and its inhabitants requires us all to work towards its long-term survival, so protecting its ecosystems with measures designed to combat climate change effects, cut pollution levels and preserve natural resources is vital for long-term viability and future generations’ wellbeing.
At a time of rapid technological development, security remains of critical importance in order to maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with technology. Protecting new innovations like biotechnology, artificial intelligence and autonomous tech is absolutely vital in order to prevent them from being misused for malicious ends and cause significant damages.
Section 4: Balancing Security and Privacy
Security and privacy remain an ever-present challenge in digital environments. Although security measures can provide important protection, they may intrude upon an individual’s personal space – an essential ingredient to maintaining free democratic societies. Finding an optimal balance is therefore imperative.
4.2 Surveillance against Civil Liberties
Recently, discussions regarding government surveillance of citizens have increased considerably. While surveillance measures aim to promote safety and fight terror attacks, breaches in privacy rights violations as well as abuses of power have lead to calls for greater transparency and accountability from authorities.
Ethical Considerations
Ethics plays an integral part in security procedures. When making decisions pertaining to surveillance, data collection or new technology applications it’s imperative that we carefully consider their ethical impacts – this way decisions respecting both individuals rights and society values can be made efficiently and ethically.
Section 5: The Future of Security
The future of security will be marked by emerging threats which continue to emerge and pose significant threats, including:
Attacks Based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI/ML attacks could become increasingly sophisticated over time and be difficult to identify, rendering threats more esoteric and difficult to combat.
Bioterrorisms: Advancements in biotechnology raise serious fears over potential uses for genetic engineering and biological agents in harmful ways against others.
Climate-related security challenges: Climate change presents security-related difficulties if it increases risks related to shortages in resources and population relocation; displacement due to diminishing natural resources may follow as conflicts erupt over diminishing supplies.
Technology will play a central role in shaping security systems over the coming years, from quantum computing and blockchain applications, through advanced encryption techniques and security-enhancing strategies, all the way up to its role as both protector and threat to current security measures in place.
Due to the interconnective nature of security threats and vulnerabilities, international cooperation is of critical importance for addressing them effectively. Collaboration must address global issues like cyber warfare, terrorism and climate change while multilateral and diplomatic agreements will play a pivotal role in maintaining global peace and security.
Conclusion
Security in its various forms has long been considered essential to modern civilization, from protecting people and nations, to information systems and environments alike. Security remains of utmost importance as we navigate the complexities of digital environments with ever-evolving threats; to maintain peace and prosperity for future generations it must continue its evolution and evolution through change, development and international cooperation.